The short-term effect of cattle exclosures on Columbia Spotted Frog (Rana luteiventris) populations and habitat in Northeastern Oregon, USA
Abstract/Summary
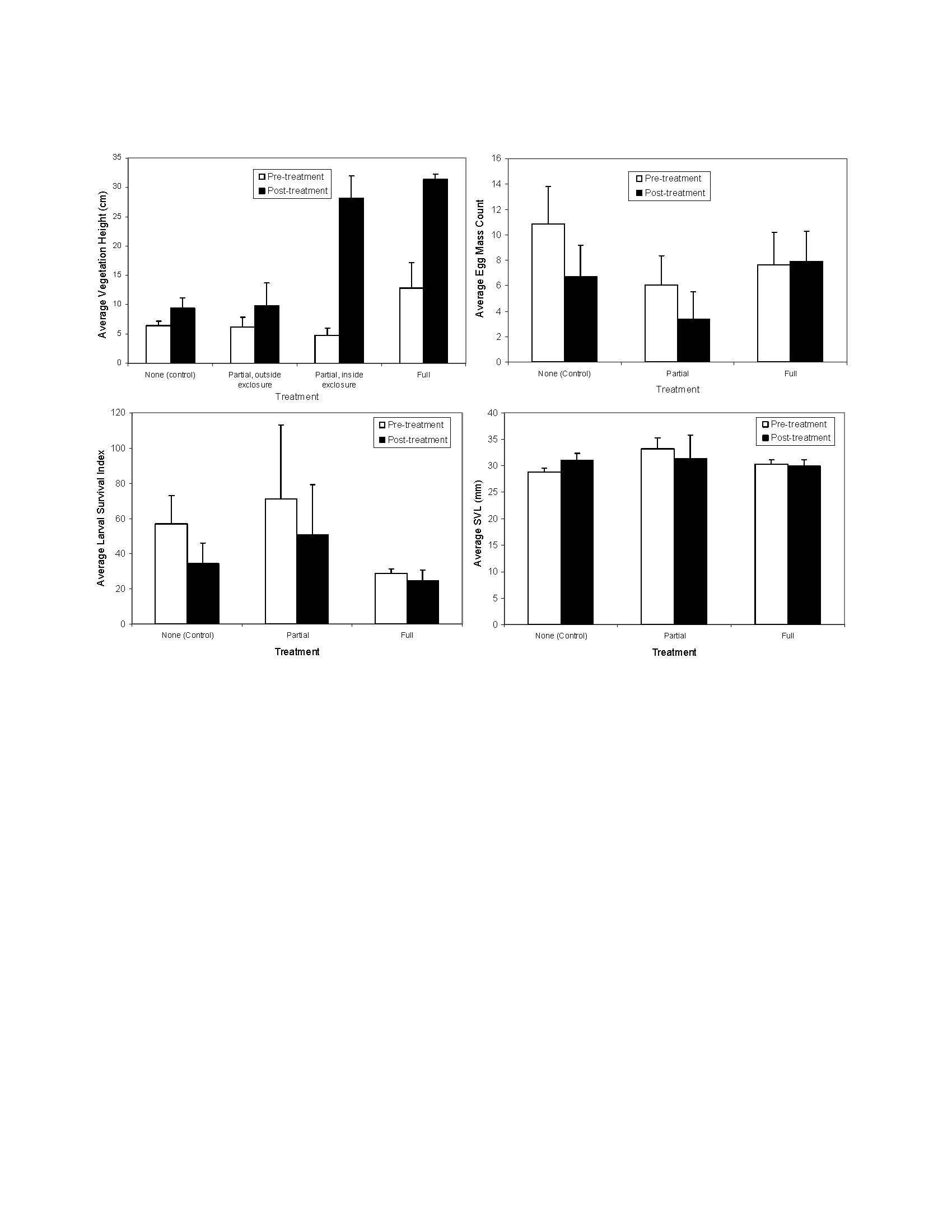
Livestock grazing is a common land use across the western USA, but concerns have been raised regarding its potential to affect amphibian populations. We studied the short-term effects of full and partial livestock grazing exclosures on Rana luteiventris (Columbia Spotted Frog) populations using a controlled manipulative field experiment with pre- and post-treatment data (2002-2006). Despite a significant increase in vegetation height within grazing exclosures, we did not find treatment effects for egg mass counts, larval survival, or size at metamorphosis 2-3 years following grazing exclosure installation. Water samples taken in late summer showed concentrations of nitrite, nitrate, ammonia and orthophosphate that were low or near detection limits across all ponds and years. The results of this experiment do not support a hypothesis that limiting cattle access to breeding ponds will help conserve R. luteiventris populations in our study area. Further research is needed to evaluate regional variation and long-term effects of grazing exclosures on R. luteiventris populations.
Publication details
| Published Date: | 2009-03-01 |
| Outlet/Publisher: | Journal of Herpetology 43: 132-138 |
| Media Format: |
ARMI Organizational Units:
Pacific Northwest - BiologyTopics:
ManagementMonitoring and Population Ecology
Place Names:
Pacific NorthwestKeywords:
grazinghabitat
land cover/land use
T&E