Geographic variation and thermal plasticity shape salamander metabolic rates under current and future climates
Abstract/Summary
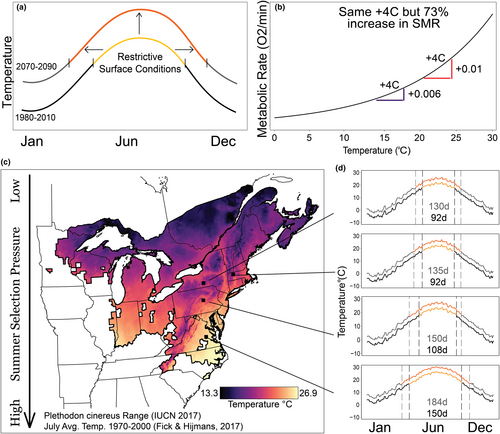
Predicted changes in global temperature are expected to increase extinction risk for ectotherms, primarily through increased metabolic rates. Higher metabolic rates generate increased maintenance energy costs which are a major component of energy budgets. Organisms often employ plastic or evolutionary (e.g. local adaptation) mechanisms to optimize metabolic rate with respect to their environment. We examined relationships between temperature and standard metabolic rate across four populations of a widespread amphibian species to determine if populations vary in metabolic response and if their metabolic rates are plastic to seasonal thermal cues. Populations from warmer climates lowered metabolic rates when acclimating to summer temperatures as compared to spring temperatures. This may act as an energy saving mechanism during the warmest time of the year. No such plasticity was evident in populations from cooler climates. Both juvenile and adult salamanders exhibited metabolic plasticity. Although some populations responded to historic climate thermal cues, no populations showed plastic metabolic rate responses to future climate temperatures, indicating there are constraints on plastic responses. We postulate that impacts of warming will likely impact the energy budgets of salamanders, potentially affecting key demographic rates, such as individual growth and investment in reproduction.
Publication details
| Published Date: | 2022-01-15 |
| Outlet/Publisher: | Ecology and Evolution |
| Media Format: |
ARMI Organizational Units:
Northeast - BiologyTopics:
DroughtSpecies and their Ecology
Place Names:
Northeast U.S.Keywords:
climate changeintraspecific variation
metabolic rate
plasticity