Search ARMI Database
Search term(s)
Contribution Number
Search Results
114 record(s) found.
Papers & Reports Preparing for a Bsal invasion into North America has improved multi-sector readiness
Papers & Reports Chytrid infections exhibit historical spread and contemporary seasonality in a declining stream-breeding frog
Papers & Reports Preparing for a Bsal invasion into North America has improved multi-sector readiness
Data Release Mercury concentrations in amphibian tissues across the United States, 2016-2021
News & Stories Climate change and Cascades Frog
A new paper by Kissel et al shows how complex life cycles interacting with climate change can lead to counter-intuitive outcomes for amphibian populations: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecochg.2023.100081
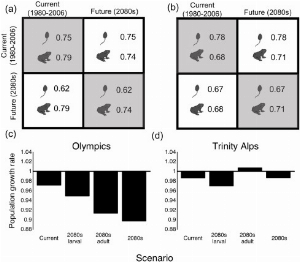
Papers & Reports Contrasting demographic responses under future climate at multiple life stages for two populations of a montane amphibian
News & Stories Do Your Halloween Plans Involve Eye of Newt? Newts Have Some Things They Want You to Know!
As first appeared in USGS NTK:
First of all, newts are not the villains, instead, they are often the victims.
Newts are at risk, along with many animals, from climate change and from disease. In fact, they could be poster animals for climate change: In southern California, recent record warm air temperatures along with peak drought conditions are linked with a 20% reduction in mean body condition (e.g., mass) in the California newt (Taricha torosa)*. The disease Batrachochytrium salamadrivorans (Bsal, literally eater of salamanders in Latin) has caused significant devastation to salamander populations in Europe. This fungal disease affects primarily newts and salamanders and the Northeastern U.S. is considered the salamander capital of the world. While Bsal is not present in the United States now**, there is serious potential for the disease to spread from Europe to the U.S. through the pet trade***.
Second, newts are quiet neighbors that contribute to society.
For example, newts eat a variety of insects, and they are eaten by birds, snakes, and some mammals.
Third, newts appreciate Halloween and keep it alive all year!
Newts have three distinct developmental life stages that are in effect, costume changes! They begin as aquatic larva, metamorphose into terrestrial juveniles (sometimes called efts), then metamorphose into adults.
And finally, newts value their eyes.
If you are really looking for some eye of newt, go look in your local grocery, “eye of newt” is actually a very un-scary and easily acquired mustard seed.
Erin Muths is a research zoologist at the Fort Collins Science Center and is a principle investigator for the Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative for the Ecosystems Mission Area. Her lab has studied boreal toads and other amphibians in the Rocky Mountains for more than 25 years. She is going to be sorcerer for Halloween.
Michael Adams is a supervisory research ecologist at the Forest and Rangeland Ecosystem Science Center and is the Lead for the Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative for the Ecosystems Mission Area. His lab has studied newts and other amphibians in the Pacific Northwest for the past 25 years. His Halloween plans are a mystery to everyone including himself.
References:
*Bucciarelli, G.M., Clark, M.A., Delaney, K.S. et al. Amphibian responses in the aftermath of extreme climate events. Sci Rep 10, 3409 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60122-2
**Waddle, J.H., Grear, D.A., Mosher, B.A., Grant, E.H.C., Adams, M.J., Backlin, A.R., Barichivich, W.J., Brand, A.B., Bucciarelli, G.M., Calhoun, D.L. and Chestnut, T., 2020. Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans (Bsal) not detected in an intensive survey of wild North American amphibians. Scientific reports 10(1), p.13012.
***Connelly, P.J., Ross, N., Stringham, O.C. and Eskew, E.A., 2023. United States amphibian imports pose a disease risk to salamanders despite Lacey Act regulations. Communications Earth & Environment, 4(1), p.351.
Papers & Reports Adjacent and downstream effects of forest harvest on the distribution and abundance of larval headwater stream amphibians in the Oregon Coast Range
Papers & Reports Broad-scale Assessment of Methylmercury in Adult Amphibians
Papers & Reports By land, air, and water – USGS science supporting fish and wildlife migrations throughout North America
Papers & Reports Broad-scale assessment of methylmercury in adult amphibians
Data Release Cascade torrent salamander (Rhyacotriton cascadae) surveys in Oregon and Washington 2022
Data Release Oregon spotted frog (Rana pretiosa) telemetry and habitat use at Crane Prairie Reservoir in Oregon, USA
Papers & Reports Looking ahead, guided by the past: The role of U.S. national parks in amphibian research and conservation
Papers & Reports Population Dynamics of the Threatened Oregon Spotted Frog (Rana pretiosa) Before and After Drought Mitigation
News & Stories Update to annotated bibliography of grazing effects on amphibians and their habitats
USGS researchers recently published an update to the 2020 ‘Annotated bibliography of grazing effects on amphibians and their habitats’ data release, a global synthesis of literature pertaining to livestock grazing effects on amphibians and their habitats. The update includes an additional 10 grazing-related publications that were released between 2020 and 2021. The data release features an interactive search tool, which has also been updated. Users of the annotated bibliography search tool can query records by user-defined criteria and output results in report format. This tool aids users in synthesizing research related to a range of specific questions and should assist land managers in evaluating and implementing grazing while maintaining habitat for wetland amphibians.
You can access the updated search tool here: https://doi.org/10.5066/P9GGPPF7