Search ARMI Database
Search term(s)
Contribution Number
Search Results
91 record(s) found.
Papers & Reports Unburned habitat essential for amphibian breeding persistence following wildfire.
Authors: Larissa L Bailey; Richard Henderson; Wendy A Estes-Zumpf; Charles Rhoades; Ellie Miller; Dominique Lujan; Erin Muths
Date: 2025 | Outlet: Global Ecology and Conservation, 57, p.e03389.
Wildfire regimes are changing rapidly with widespread increase in the intensity, frequency, and duration of fire activity, especially in the western United States. Limited studies explore the impacts of wildfires on aquatic taxa and few focus on lentic habitats that are essential for amphibians, many of which are of conservation concern. We capitalized on existing pre-fire surveys for anuran species and resurveyed a random subset of wetlands across a gradient of soil burn severity to investigate the short-term effects of wildfire on a relict population of wood frogs in the southern Rocky Mountains. We also investigated whether maps created to support rapid post-fire emergency response activities (i.e., USFS BAER program) accurately characterize soil burn severity around small habitat features (i.e., ponds) that serve as important amphibian breeding and rearing habitat. We found that wood frog breeding persistence following fires was strongly influenced by the percentage of their terrestrial habitat (100m buffer surrounding breeding ponds) that was burned. Wood frog colonization probability of previously unoccupied ponds was low (~ 0.10) and unaffected by soil burn severity. Importantly, we found that remotely sensed data typically produced to predict flooding and erosion at broad (catchment) scales is a poor representation of the amount and variation in soil burn severity surrounding small habitat features (e.g., ponds), suggesting that additional field sampling is necessary to understand wildfire responses for species that rely on small habitat features. Understanding short-term geographic- and species-specific variation in response to wildfires provides the basis to explore time to recovery (e.g., when wood frogs return to burned breeding sites) or to determine if declines in breeding distributions intensify over time.
Papers & Reports Effects of harmful algal blooms on amphibians and reptiles are underreported and underrepresented
Authors: Brian J Tornabene; Kelly L Smalling; Blake R Hossack
Date: 2024-07-05 | Outlet: Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) are a persistent and increasing problem globally, yet we still have a limited knowledge about how they affect many wildlife. Although semi-aquatic and aquatic amphibians and reptiles have experienced large declines and occupy environments where HABs are increasingly problematic, their vulnerability to HABs remains unclear. To inform monitoring, management, and future studies, we conducted a literature review and synthesized studies and reported mortality events describing effects of cyanotoxins from HABs on freshwater herpetofauna. Our review identified 37 unique studies and 71 endpoints (no-observed-effect and lowest-observed-effect concentrations) involving 11 amphibian and three reptile species worldwide. Responses varied widely among studies, species, and concentrations used in experiments. Concentrations causing lethal and sublethal effects in experiments were generally 1–100 µg/L, which is near the mean value of reported events but 70times less than the maximum cyanotoxin concentrations reported in the environment. However, one species of amphibian was tolerant to concentrations of 10,000 µg/L, demonstrating potentially immense differences in sensitivities. Most studies focused on microcystin-LR (MC-LR), which can increase systemic inflammation and harm the digestive system, reproductive organs, liver and kidneys, and development. The few studies on other cyanotoxins illustrated that effects resembled those of MC-LR at similar concentrations, but more research is needed to describe effects. All experimental studies were on larval and adult amphibians; there were no such studies on reptiles. Experimental work with reptiles and adult amphibians is needed to clarify thresholds of tolerance. Only nine mortality events were reported, mostly for reptiles. Given that amphibians likely decay faster than reptiles, which have tissues that resists decomposition, mass amphibian mortality events from HABs have likely been underreported. We propose seven major areas to focus future efforts to enhance our understanding of effects and monitoring of HABs on herpetofauna that fill important roles in freshwater and terrestrial environments.
Papers & Reports Native amphibian toxin reduces invasive crayfish feeding with potential benefits to stream biodiversity
Authors: Gary Bucciarelli; Sierra J. Smith; Justin J. Choe; Phoebe D. Shin; Robert N Fisher; Lee B Kats
Date: 2023-09-13 | Outlet: BMC Ecology and Evolution 23, 51
Biodiversity is generally reduced when non-native species invade an ecosystem. Invasive crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, populate California freshwater streams, and in the Santa Monica Mountains (Los Angeles, USA), their introduction has led to trophic cascades due to omnivorous feeding behavior and a rapid rate of population growth. The native California newt, Taricha torosa, possesses a neurotoxin, tetrodotoxin (TTX), that affects freshwater animal behavior. Given P. clarkii has a limited evolutionary history with TTX, we hypothesized that TTX may affect crayfish feeding behaviors. To determine if TTX affects P. clarkii behavior, we measured cumulative movement and various feeding behaviors of P. clarkii exposed to (i) waterborne, ecologically realistic concentrations of TTX (~?3.0?×?10??8 moles/L), (ii) an anuran chemical cue to account for intraguild cues, or (iii) a T. torosa chemical cue with quantitated TTX in it (~?6.2?×?10??8 moles/L).
Results
We found that the presence of TTX in any form significantly reduced crayfish movement and decreased the amount of food consumed over time. Crayfish responses to the anuran treatment did not significantly differ from controls.
Conclusion
Our laboratory results show that naturally occurring neurotoxin from native California newts limits invasive crayfish foraging and feeding rates, which may play a role in preserving local stream ecosystems by limiting invasive crayfish behaviors that are detrimental to biodiversity.
Results
We found that the presence of TTX in any form significantly reduced crayfish movement and decreased the amount of food consumed over time. Crayfish responses to the anuran treatment did not significantly differ from controls.
Conclusion
Our laboratory results show that naturally occurring neurotoxin from native California newts limits invasive crayfish foraging and feeding rates, which may play a role in preserving local stream ecosystems by limiting invasive crayfish behaviors that are detrimental to biodiversity.
Papers & Reports Population Dynamics of the Threatened Oregon Spotted Frog (Rana pretiosa) Before and After Drought Mitigation
Authors: Jennifer C Rowe; Christopher A Pearl; Adam Duarte; Brome McCreary; Michael J Adams
Date: 2023-09-22 | Outlet: The Journal of Wildlife Management
Amphibians are among the most sensitive taxa to climate change, and species inhabiting arid and semiarid landscapes at the extremes of their range are especially vulnerable to drought. The Jack Creek, Oregon, USA, population of Oregon spotted frogs (Rana pretiosa) faces unique challenges because it occupies the highest elevation site in the species' extant range and one that has been transformed by loss of American beavers (Castor canadensis[/]), which historically maintained open water. We evaluated the effects of drought mitigation (addition of excavated ponds) on relationships between local and regional water availability, inactive legacy beaver dams, and Oregon spotted frog population dynamics in the Jack Creek system. We conducted egg mass surveys and capture-mark-recapture sampling at a treatment reach with excavated ponds and 3 reference reaches over 13 years; surveys spanned a period before and after pond excavation at the treatment and 1 primary comparison reference reach. We analyzed data using a combination of robust design capture-mark-recapture estimators and generalized linear mixed models to characterize population dynamics. Adult Oregon spotted frog survival was approximately 19.5% higher at the treatment reach than the primary reference reach during the study period. Annual survival was most strongly associated with late summer vegetation greenness, a proxy for water availability, and males had higher survival than females. Among the 4 study reaches, the treatment reach consistently had higher late summer vegetation greenness, and the hydrology functioned more independently of regional precipitation patterns relative to the reference reaches; however, these dynamics were not linked to pond excavation. Breeding was concentrated in 2 legacy beaver ponds that were deepened by excavation during the study compared to an unexcavated beaver pond, 2 excavated ponds without legacy beaver dams, and 9 reference ponds. These results point to the benefit of enhancing existing beaver structures and indicate that management actions aimed at maintaining surface water for breeding in spring and saturated soils and ponded water for adults in late summer would benefit this unique population of Oregon spotted frogs in the face of drought.
Papers & Reports Disentangling direct and indirect effects of extreme events on coastal wetland communities
Authors: Courtney L Davis; Susan C Walls; William J Barichivich; Mary E Brown; David AW Miller
Date: 2022-12-16 | Outlet: Journal of Animal Ecology
1. One of the primary ways in which climate change will impact coastal freshwater wetlands is through changes in the frequency, intensity, timing, and distribution of extreme weather events. Disentangling the direct and indirect mechanisms of population- and community-level responses to extreme events is vital to predicting how species composition of coastal wetlands will change under future conditions.
2. We extended static structural equation modeling approaches to incorporate system dynamics in a multi-year multispecies occupancy model to quantify the effects of extreme weather events on a coastal freshwater wetland system.
3. We used data from an 8-year study (2009 to 2016) on St. Marks National Wildlife Refuge in Florida, USA, to quantify species-specific and community-level changes in amphibian and fish occupancy associated with two flooding events in 2012 and 2013. We examine how physical changes to the landscape, including potential changes in salinity and increased wetland connectivity, may have contributed to or exacerbated the effects of these extreme weather events on the biota of isolated coastal wetlands.
4. We provide evidence that the primary effects of flooding on the amphibian community were through indirect mechanisms via changes in the composition of the sympatric fish community that may have had lethal (i.e., through direct predation) or non-lethal (i.e., through direct or indirect competitive interactions) effects. In addition, we shown that amphibian species differed in their sensitivity to direct flooding effects and indirect changes in the fish community and wetland specific conductance, which led to variable responses across the community. These effects led to the overall decline in amphibian species richness from 2009 to 2016, suggesting that wetland-breeding amphibian communities on St. Marks may not be resilient to predicted changes in coastal disturbance regimes as a result of climate change.
5. Understanding both direct and indirect effects, as well as species interactions, is important for predicting the effects of a changing climate on individual species, communities, and ecosystems.
2. We extended static structural equation modeling approaches to incorporate system dynamics in a multi-year multispecies occupancy model to quantify the effects of extreme weather events on a coastal freshwater wetland system.
3. We used data from an 8-year study (2009 to 2016) on St. Marks National Wildlife Refuge in Florida, USA, to quantify species-specific and community-level changes in amphibian and fish occupancy associated with two flooding events in 2012 and 2013. We examine how physical changes to the landscape, including potential changes in salinity and increased wetland connectivity, may have contributed to or exacerbated the effects of these extreme weather events on the biota of isolated coastal wetlands.
4. We provide evidence that the primary effects of flooding on the amphibian community were through indirect mechanisms via changes in the composition of the sympatric fish community that may have had lethal (i.e., through direct predation) or non-lethal (i.e., through direct or indirect competitive interactions) effects. In addition, we shown that amphibian species differed in their sensitivity to direct flooding effects and indirect changes in the fish community and wetland specific conductance, which led to variable responses across the community. These effects led to the overall decline in amphibian species richness from 2009 to 2016, suggesting that wetland-breeding amphibian communities on St. Marks may not be resilient to predicted changes in coastal disturbance regimes as a result of climate change.
5. Understanding both direct and indirect effects, as well as species interactions, is important for predicting the effects of a changing climate on individual species, communities, and ecosystems.
Papers & Reports Cryptic declines of small, cold-water specialists highlight potential vulnerabilities of headwater streams as climate refugia
Authors: Blake R Hossack; M LeMoine; Emily B Oja; Lisa A Eby
Date: 2023 | Outlet: Biological Conservation
Increasing temperatures and climate-driven disturbances like wildfire are a growing threat to many species,
including cold-water specialists. Montane areas and cold streams are often considered climate refugia that buffer
communities against change. However, climate refugia are often species-specific, and despite growing awareness
that life histories and habitat requirements shape responses to change, small or non-game species are often
under-represented in monitoring and planning programs. A recent study in Montana, USA, revealed much larger
warming-related declines in occupancy for small, non-game slimy sculpin (Cottus cognatus) between 1993 and
1995 and 2011–2013 than for two socially valued salmonid fishes that shape regional conservation efforts. To
broaden insight into climate change vulnerabilities of headwater stream communities, we analyzed data for
Rocky Mountain tailed frogs (Ascaphus montanus) that were collected during those same electrofishing surveys
for fishes from 241 stream reaches. Tailed frogs occupy small, cold streams and have several life-history traits
that make them sensitive to environmental change. We used a Bayesian framework to estimate occupancy,
colonization, and extinction dynamics relative to forest canopy, estimated stream temperature, and wildfire
effects. Tailed frog occupancy decreased by 19 % from 1993 to 1995 to 2011–2013. Changes in occupancy were
linked with increased extinction and reduced colonization where there were fire-driven reductions in canopy
cover, and reduced colonization of stream reaches that warmed on average 0.8 ?C during the study. Our results
highlight extensive extirpations for oft-overlooked species and emphasize the importance of including species
with diverse habitat requirements and life histories in conservation planning.
including cold-water specialists. Montane areas and cold streams are often considered climate refugia that buffer
communities against change. However, climate refugia are often species-specific, and despite growing awareness
that life histories and habitat requirements shape responses to change, small or non-game species are often
under-represented in monitoring and planning programs. A recent study in Montana, USA, revealed much larger
warming-related declines in occupancy for small, non-game slimy sculpin (Cottus cognatus) between 1993 and
1995 and 2011–2013 than for two socially valued salmonid fishes that shape regional conservation efforts. To
broaden insight into climate change vulnerabilities of headwater stream communities, we analyzed data for
Rocky Mountain tailed frogs (Ascaphus montanus) that were collected during those same electrofishing surveys
for fishes from 241 stream reaches. Tailed frogs occupy small, cold streams and have several life-history traits
that make them sensitive to environmental change. We used a Bayesian framework to estimate occupancy,
colonization, and extinction dynamics relative to forest canopy, estimated stream temperature, and wildfire
effects. Tailed frog occupancy decreased by 19 % from 1993 to 1995 to 2011–2013. Changes in occupancy were
linked with increased extinction and reduced colonization where there were fire-driven reductions in canopy
cover, and reduced colonization of stream reaches that warmed on average 0.8 ?C during the study. Our results
highlight extensive extirpations for oft-overlooked species and emphasize the importance of including species
with diverse habitat requirements and life histories in conservation planning.
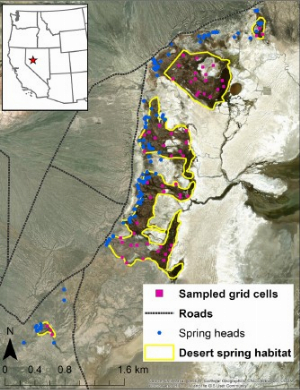
Papers & Reports Hot, wet, and rare: modeling the occupancy dynamics of the narrowly distributed Dixie Valley Toad
Authors: Jonathan P Rose; Patrick M Kleeman; Brian J Halstead
Date: 2022-08-29 | Outlet: Wildlife Research
Small population sizes and no possibility of metapopulation rescue put narrowly distributed endemic species under elevated risk of extinction from anthropogenic change. Desert spring wetlands host many endemic species that require aquatic habitat and are isolated by the surrounding xeric terrestrial habitat. Aims. We sought to model the occupancy dynamics of the Dixie Valley toad (Anaxyrus williamsi), a recently described species endemic to a small desert spring wetland complex in Nevada, USA. Methods. We divided the species’ range into 20 m × 20 m cells and surveyed for Dixie Valley toads at 60 cells during six primary periods from 2018 to 2021, following an occupancy study design. We analysed our survey data by using a multi-state dynamic occupancy model to estimate the probability of adult occurrence, colonisation, site survival, and larval occurrence and the relationship of each to environmental covariates. Key results. The detection probabilities of adult and larval toads were affected by survey length and time of day. Adult Dixie Valley toads were widely distributed, with detections in 75% of surveyed cells at some point during the 3-year study, whereas larvae were observed only in 20% of cells during the study. Dixie Valley toad larvae were more likely to occur in cells far from spring heads with a high coverage of surface water, low emergent vegetation cover, and water temperatures between 20°C and 28°C. Adult toads were more likely to occur in cells with a greater coverage of surface water and water depth >10 cm. Cells with more emergent vegetation cover and surface water were more likely to be colonised by adult toads. Conclusions. Our results showed that Dixie Valley toads are highly dependent on surface water in both spring and autumn. Adults and larvae require different environmental conditions, with larvae occurring farther from spring heads and in fewer cells. Implications. Disturbances to the hydrology of the desert spring wetlands in Dixie Valley could threaten the persistence of this narrowly distributed toad.
Papers & Reports Looking ahead, guided by the past: The role of U.S. national parks in amphibian research and conservation
Authors: Brian J Halstead; Andrew M Ray; Erin Muths; Evan HC Grant; Rob L Grasso; Michael J Adams; Katy S Delaney; Jane Carlson; Blake R Hossack
Date: 2022-03 | Outlet: Ecological Indicators
Protected areas like national parks are essential elements of conservation because they limit human influence on the landscape, which protects biodiversity and ecosystem function. The role of national parks in conservation, however, often goes far beyond limiting human influence. The U.S. National Park Service and its system of land units contribute substantively to conservation by providing protected lands where researchers can document trends in species distributions and abundances, examine characteristics important for generating these trends, and identify and implement conservation strategies to preserve biodiversity. We reviewed the contribution of U.S. national parks to amphibian research and conservation and highlight important challenges and findings in several key areas. First, U.S. national parks were instrumental in providing strong support that amphibian declines were real and unlikely to be simply a consequence of habitat loss. Second, research in U.S. national parks provided evidence against certain hypothesized causes of decline, like UV-B radiation, and evidence for others, such as introduced species and disease. However, describing declines and identifying causes contributes to conservation only if it leads to management; importantly, U.S. national parks have implemented many conservation strategies and evaluated their effectiveness in recovering robust amphibian populations. Among these, removal of invasive species, especially fishes; conservation translocations; and habitat creation and enhancement stand out as examples of successful conservation strategies with broad applicability. Successful management for amphibians is additionally complicated by competing mandates and stakeholder interests; for example, past emphasis on increasing visitor enjoyment by introducing fish to formerly fishless lakes had devastating consequences for many amphibians. Other potential conflicts with amphibian conservation include increasing development, increased risk of introductions of disease and exotic species with increased visitation, and road mortality. Decision science and leveraging partnerships have proven to be key components of effective conservation under conflicting mandates in national parks. As resource managers grapple with large-scale drivers that are outside local control, public-private partnerships and adaptive strategies are increasing in importance. U.S. national parks have played an important role in many aspects of identifying and ameliorating the amphibian decline crisis and will continue to be essential for the conservation of amphibians in the future.
Papers & Reports Energy-related wastewater contamination alters microbial communities of sediment, water, and amphibian skin
Authors: Brian J Tornabene; Kelly L Smalling; C E Givens; Emily B Oja; Blake R Hossack
Date: 2023-07-01 | Outlet: Science of the Total Environment
To inform responsible energy development, it is important to understand the ecological effects of contamination events. Wastewaters from oil and gas extraction often contain high concentrations of sodium chloride (NaCl) and heavy metals (e.g., strontium and vanadium), but studies of their influence on microbial communities are limited. We sampled water, sediment, and larval amphibian skin (four species) across a gradient of contamination (0.04–17500 mg/L Cl) in a large energy production area of North America. NaCl concentrations affected the similarity among microbiomes of water, sediment, and amphibian skin, but not the diversity or richness of water and skin microbiomes. Strontium concentrations were associated with lower diversity and richness of sediment microbial communities. Amphibian microbiomes were similar to those of water, but not sediment, and sediment microbiomes were similar to those of water. Species identity was the strongest predictor of amphibian microbiomes; frog microbiomes were similar but differed from that of the salamander, whose microbiome had the lowest richness and diversity. Understanding whether effects of wastewaters on microbial communities also influences their ecosystem function will be an important next step. Our study provides novel insight into associations among different wetland microbial communities and effects of wastewaters from energy production.
Papers & Reports Late-season movement and habitat use by Oregon spotted frog (Rana pretiosa) in a large reservoir in Oregon, USA
Authors: Christopher A Pearl; Jennifer C Rowe; Brome McCreary; Michael J Adams
Date: 2022-03-04 | Outlet: Journal of Herpetology
Dam-created reservoirs are common landscape features that can provide habitat for amphibians, but their water level fluctuations and nonnative predators can differ markedly from more natural habitats. We compared fall movement and habitat use by the Oregon Spotted Frog (Rana pretiosa) in the reservoir pool with nearby river and pond habitats at Crane Prairie Reservoir in central Oregon, USA. Movement rate of frogs in the river and ponds declined as water temperature cooled. Reservoir frogs moved further than those in the river or ponds, and their movement rate increased as water temperature cooled. Most frog locations across all site types were in aquatic herbaceous vegetation. We did not find shifts in habitat between early and late fall. Increased movement and the lack of habitat shift in our reservoir frogs deeper into fall contrast with R. pretiosa in non-reservoir sites in this study and others. Consistent use of vegetation by reservoir frogs throughout the fall could indicate cover use in presence of fish predators. Our study provides additional detail on the range of habitats used by R. pretiosa in fall and suggests areas for further work to improve survival in constructed sites with abundant fish predators.
Papers & Reports Testing whether adrenal steroids mediate phenotypic and physiologic effects of elevated salinity on larval tiger salamanders
Authors: Brian J Tornabene; E J Crespi; Creagh W Breuner; Blake R Hossack
Outlet: Integrative Zoology
Salinity (sodium chloride, NaCl) from anthropogenic sources is a persistent contaminant that negatively affects freshwater taxa. Amphibians can be susceptible to salinity, but some species are innately or adaptively tolerant. Physiological mechanisms mediating tolerance to salinity are still unclear, but changes in osmoregulatory hormones such as corticosterone (CORT) and aldosterone (ALDO) are prime candidates. We exposed larval barred tiger salamanders (Ambystoma mavortium) to environmentally relevant NaCl treatments (<32–4000 mg·L?1) for 24 days to test effects on growth, survival, and waterborne CORT responses. Of those sampled, we also quantified waterborne ALDO from a subset. Using a glucocorticoid antagonist (RU486), we also experimentally suppressed CORT signaling of some larvae to determine if CORT mediates effects of salinity. There were no strong differences in survival among salinity treatments, but salinity reduced dry mass, snout–vent length, and body condition while increasing water content of larvae. High survival and sublethal effects demonstrated that salamanders were physiologically challenged but could tolerate the experimental concentrations. CORT signaling did not attenuate sublethal effects of salinity. Baseline and stress-induced (after an acute stressor, shaking) CORT were not influenced by salinity. ALDO was correlated with baseline CORT, suggesting it could be difficult to decouple the roles of CORT and ALDO. Future studies comparing ALDO and CORT responses of adaptively tolerant and previously unexposed populations could be beneficial to understand the roles of these hormones in tolerance to salinity. Nevertheless, our study enhances our understanding of the roles of corticosteroid hormones in mediating effects of a prominent anthropogenic stressor.
Papers & Reports Effects of salinity and RU486 on waterborne aldosterone and corticosterone of larval northern leopard frog larvae
Authors: Brian J Tornabene; Creagh W Breuner; Blake R Hossack; E J Crespi
Date: 2022-02-01 | Outlet: General and Comparative Endocrinology
testIncreased salinity is an emerging contaminant of concern for aquatic taxa. For amphibians exposed to salinity, there is scarce information about the physiological effects and changes in osmoregulatory hormones such as corticosterone (CORT) and aldosterone (ALDO). Recent studies have quantified effects of salinity on CORT physiology of amphibians based on waterborne hormone collection methods, but much less is known about ALDO in iono- and osmoregulation of amphibians. We re-assayed waterborne hormone samples from a previous study to investigate effects of salinity (sodium chloride, NaCl) and a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist (RU486) on ALDO of northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens) larvae. We also investigated relationships between ALDO and CORT. Waterborne ALDO marginally decreased with increasing salinity and was, unexpectedly, positively correlated with baseline and stress-induced waterborne CORT. Importantly, ALDO increased when larvae were exposed to RU486, suggesting that RU486 may also suppress mineralocorticoid receptors or that negative feedback of ALDO is mediated through glucocorticoid receptors. Alternatively, CORT increases with RU486 treatment and might be a substrate for ALDO synthesis, which could account for increases in ALDO with RU486 treatment and the correlation between CORT and ALDO. ALDO was negatively correlated with percent water, such that larvae secreting more ALDO retained less water. Although sample sizes were limited and further validation and studies are warranted, our findings expand our understanding of adrenal steroid responses to salinization in amphibians and proposes new hypotheses regarding the co-regulation of ALDO and CORT.
Papers & Reports Impacts of a Non-indigenous Ecosystem Engineer, the American Beaver (Castor canadensis), in a Biodiversity Hotspot
Authors: Jonathan Q Richmond; Camm C. Swift; Thomas A. Wake; Cheryl S Brehme; Kristine L Preston; Barbara E. Kus; Edward L Ervin; S Tremor; Tritia Matsuda; Robert N Fisher
Date: 2021-11-18 | Outlet: Frontiers in Conservation Science 2:752400
Non-native species having high per capita impacts in invaded communities are those that modulate resource availability and alter disturbance regimes in ways that are biologically incompatible with the native biota. In areas where it has been introduced by humans, American beaver (Castor canadensis) is an iconic example of such species due to its capacity to alter trophic dynamics of entire ecosystems and create new invasional pathways for other non-native species. The species is problematic in several watersheds within the Southern California-Northern Baja California Coast Ecoregion, a recognized hotspot of biodiversity, due to its ability to modify habitat in ways that favor invasive predators and competitors over the region's native species and habitat. Beaver was deliberately introduced across California in the mid-1900s and generally accepted as non-native to the region up to the early 2000s; however, articles promoting the idea that beaver may be a natural resident have gained traction in recent years, due in large part to the species' charismatic nature rather than by presentation of sound evidence. Here, we discuss the problems associated with beaver disturbance and its effects on conserving the region's native fauna and flora. We refute arguments underlying the claim that beaver is native to the region, and review paleontological, zooarchaeological, and historical survey data from renowned field biologists and naturalists over the past ~160 years to show that no evidence exists that beaver arrived by any means other than deliberate human introduction. Managing this ecosystem engineer has potential to reduce the richness and abundance of other non-native species because the novel, engineered habitat now supporting these species would diminish in beaver-occupied watersheds. At the same time, hydrologic functionality would shift toward more natural, ephemeral conditions that favor the regions' native species while suppressing the dominance of the most insidious invaders.
Papers & Reports Corticosterone Mediates a Growth-Survival Tradeoff for an Amphibian Exposed to Increased Salinity
Authors: Brian J Tornabene; Blake R Hossack; E J Crespi; Creagh W Breuner
Date: 2021-08-09 | Outlet: Journal of Experimental Zoology Part A
Life-history tradeoffs are common across taxa, but growth-survival tradeoffs—which usually enhance survival at a cost to growth—are less frequently investigated. Increased salinity (NaCl) is a prevalent anthropogenic disturbance that may cause a growth-survival tradeoff for amphibians. Although physiological mechanisms mediating tradeoffs are seldom investigated, hormones are prime candidates. Corticosterone (CORT) is a steroid hormone that independently influences survival and growth and may provide mechanistic insight into growth-survival tradeoffs. We used 24-d trials to test effects of salinity (0 – 4000 mg/L Cl-) on growth, development, survival, CORT responses, and tradeoffs among traits of larval Northern Leopard Frogs (Rana pipiens). We also tested experimentally suppressed CORT signaling to determine whether CORT signaling mediates effects of salinity and life history tradeoffs . Increased salinity reduced survival, growth, and development. Suppressing CORT signaling in conjunction with salinity reduced survival further, but also attenuated negative effects of salinity on growth and development. CORT of control larvae increased or was stable with growth and development, but decreased with growth and development for those exposed to salinity. Therefore, salinity dysregulated CORT physiology. Across all treatments, larvae that survived had higher CORT than larvae that died. By manipulating CORT signaling, we provide strong evidence that CORT physiology mediates the outcome of a growth-survival tradeoff. To our knowledge, this is the first study to concomitantly measure tradeoffs between growth and survival and experimentally link these changes to CORT physiology. Identifying mechanistic links between stressors and fitness-related outcomes is critical to enhance our understanding of tradeoffs.
Papers & Reports Assessing the ecological functionality and integrity of natural ponds, excavated ponds and stormwater basins for conserving amphibian diversity
Authors: Kelly L Smalling; Sara E Breitmeyer; John F Bunnell; Kim J Laidig; Patrick M Burritt; Marilyn C Sobel; Jonathan A Cohl; Michelle L Hladik; Kristin M Romanok; Paul M Bradley
Date: 2012-08-20 | Outlet: Global Ecology and Conservation 30, e01765
Wetlands provide ecological functionality by maintaining and promoting regional biodiversity supporting quality habitat for aquatic organisms. Globally, habitat loss, fragmentation and degradation due to increases in agricultural activities and urban development have reduced or altered geographically isolated wetlands, thus reducing biodiversity. The objective of this study was to assess the relative ecological function and integrity of natural ponds, excavated ponds and stormwater basins for amphibian diversity in the New Jersey Pinelands, USA by comparing hydrologic conditions, water quality, pesticide concentrations (water, sediment and tissue) and plant and anuran assemblages. Twenty-four wetlands were selected based on surrounding land-use and sampled for a variety of abiotic and biotic variables. Abiotic and biotic wetland variables were similar between natural and excavated ponds, with notable differences between the ponds and stormwater basins. Natural and excavated ponds displayed characteristic Pinelands water quality (low pH, high organic carbon, and low pesticide concentrations), exhibited high ecological integrity and supported native anuran species. Stormwater basins and degraded ponds surrounded by altered land-use exhibited degraded water quality (high pH, high pesticide concentrations) and were dominated by non-native and introduced plant and anuran species. Results from this study can broadly inform resource conservation strategies for amphibians and other communities with a diverse range of habitat requirements, particularly in areas where conservation and development are competing priorities. To conserve biodiversity in changing landscapes, wetlands with similar functionality and land-use characteristics need to be identified and managed to preserve water quality for species of conservation concern.
Papers & Reports Demography of the Oregon spotted frog along a hydrologically modified river
Authors: Jennifer C Rowe; Adam Duarte; Christopher A Pearl; Brome McCreary; P K Haggerty; John W Jones; Michael J Adams
Date: 2021-06-21 | Outlet: Ecosphere
Altered flow regimes can contribute to dissociation between life history strategies and environmental conditions, leading to reduced persistence reported for many wildlife populations inhabiting regulated rivers. The Oregon spotted frog (Rana pretiosa) is a threatened species occurring in floodplains, ponds, and wetlands in the Pacific Northwest with a core range in Oregon, USA. All life stages of R. pretiosa are reliant on aquatic habitats, and inundation patterns across the phenological timeline can have implications for population success. We conducted capture-mark-recapture (CMR) sampling of adult and subadult R. pretiosa at three sites along the Deschutes River downstream from two dams that regulate flows. We related the seasonal extent of inundated habitat at each site to monthly survival probabilities using a robust design CMR model. We also developed matrix projection models to simulate population dynamics into the future under current river flows. Monthly survival was strongly associated with the extent and variability of inundated habitat, suggesting some within-season fluctuations at higher water levels could be beneficial. Seasonal survival was lowest in the winter for all three sites, owing to limited water availability and the greater number of months within this season relative to other seasons. Population growth for the two river-connected sites was most strongly linked to adult survival, whereas population growth at the river-disconnected site was most strongly tied to survival in juvenile stages. This research identifies population effects of seasonally limited water and highlights conservation potential of enhancing survival of particularly influential life stages.
Papers & Reports Water Temperature and Availability Shape the Spatial Ecology of a Hot Springs Endemic Toad (Anaxyrus williamsi)
Authors: Brian J Halstead; Patrick M Kleeman; Jonathan P Rose; Kristen J Fouts
Date: 2021-02-26 | Outlet: Herpetologica
Desert amphibians are limited to exploiting ephemeral resources and aestivating or to inhabiting scarce refuges of permanent water, such as springs. Understanding how amphibians use these resources is essential for their conservation. Dixie Valley Toads (Anaxyrus williamsi) are precinctive to a small system of cold and hot springs in the Dixie Valley, Nevada, USA. The toads have been petitioned for listing under the US Endangered Species Act, and information about how they use terrestrial and aquatic resources will help managers to conserve the toads and identify threats like geothermal energy development that might affect these toads. We used radiotelemetry to study the seasonal home ranges, movements, and habitat associations of Dixie Valley Toads in autumn 2018 and spring 2019. We found that toads were very closely associated with water in both seasons, with most observations occurring in water, especially for males in spring and all toads in the autumn. Even when found in terrestrial habitat, toads were a median distance of 4.2 m (95% credible interval = 3.3–5.3) from water; 95% of the time in spring and autumn, toads were within 14 m of water. Dixie Valley Toad habitat selection indicated a similar pattern, with selection in both spring and autumn for locations closer to water and for warmer water and substrates than at nearby available locations. In autumn, toads also avoided bare ground and terrestrial graminoids. Dixie Valley Toads selected brumation sites in, over (within dense vegetation), or near water, often near springs where water depths and temperatures are likely stable through the winter. The reliance of Dixie Valley Toads on water in spring, autumn, and during brumation suggests that alteration to historical flows and water temperatures are likely to affect the toads. Changes to the hydrothermal environment when toads are brumating could be particularly detrimental, potentially killing inactive toads.
Papers & Reports Estimating the survival of unobservable life stages for a declining frog with a complex life-history.
Authors: Jonathan P Rose; Sarah J Kupferberg; Clara A Wheeler; Patrick M Kleeman; Brian J Halstead
Date: 2021-02-15 | Outlet: Ecosphere 12(2):e03381
Demographic models enhance understanding of drivers of population growth and inform conservation efforts to prevent population declines and extinction. For species with complex life histories, however, parameterizing demographic models is challenging because some life stages can be dif?cult to study directly. Integrated population models (IPMs) empower researchers to estimate vital rates for organisms that have cryptic or widely dispersing early life stages by integrating multiple demographic data sources. For a stream-inhabiting frog(Rana boylii) that is declining through much of its range in Oregon and California, USA, we collected egg-mass counts and capture–mark–recapture data on adults from two populations in California to ?t IPMs that estimate adult abundance and the survival rate of both marked and unobserved life stages. Estimates of adult abundance based on long-term monitoring of egg-mass counts showed that study populations ?uctuated greatly inter-annually but were stable at longer timescales (i.e., decades). Adult female survival during 5–6 yr of capture–mark–recapture study periods was nearly equal in each population. Survival rate of R. boylii eggs to the subadult stage is low on average (0.002) but highly variable among years depending on post-oviposition stream ?ow. Population viability analysis showed that survival of adult and subadult life stages has the greatest proportional effect on population growth; the survival of egg and tadpole life stages, however, is more malleable by management interventions. For example, simulations showed head-starting of tadpoles, salvaging stranded egg masses, and limiting aseasonal pulsed ?ows could dramatically reduce the threat of extirpation. This study demonstrates the value of integrating multiple demographic data sources to construct models of population dynamics in species with complex life histories.
Papers & Reports Baseline Conditions and Projected Future Hydro-Climatic Change in National Parks in the Conterminous United States
Authors: William A Battaglin
Date: 2020-06-15 | Outlet: Water 2020, 12(6), 1704; https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061704
Abstract: The National Park Service (NPS) manages hundreds of parks in the United States, and many contain important aquatic ecosystems and/or threatened and endangered aquatic species vulnerable to hydro-climatic change. More effective management of park resources under future hydro-climatic uncertainty requires information on both baseline conditions and the range of projected future conditions. A monthly water balance model was used to assess baseline (1981–1999) conditions and a range of projected future hydro-climatic conditions in 374 NPS parks. General circulation model outputs representing 214 future climate simulations were used to drive the model. Projected future changes in air temperature (T), precipitation (p), and runoff (R) are expressed as departures from historical baselines. Climate simulations indicate increasing T by 2030 for all parks with 50th percentile simulations projecting increases of https://1.67 °C or more in 50% of parks. Departures in 2030 p indicate a mix of mostly increases and some decreases, with 50th percentile simulations projecting increases in p in more than 70% of parks. Departures in R for 2030 are mostly decreases, with the 50th percentile simulations projecting decreases in R in more than 50% of parks in all seasons except winter. Hence, in many NPS parks, R is projected to decrease even when p is projected to increase because of increasing T in all parks. Projected changes in future hydro-climatic conditions can also be assessed for individual parks, and Rocky Mountain National Park and Congaree National Park are used as examples.
Papers & Reports Effects of experimental warming and nutrient enrichment on wetland communities at the Arctic’s edge
Authors: J M Davenport; L Fishback; Blake R Hossack
Date: 2020-09 | Outlet: Hydrobiologia
The disproportionate effects of warming for high-latitude, freshwater ecosystems has been well documented, but in some areas, changes have been further impacted by human-subsidized increases of waterfowl. To gain insight into how predicted changes in temperature and nutrient inputs might affect ecosystem function, we conducted a mesocosm experiment in the Canadian Subarctic with three levels of simulated goose enrichment and warming to measure changes in size and survival of larval wood frogs and boreal chorus frogs and primary productivity (phytoplankton and periphyton biomass). Our results highlight that the consequences of these rapid changes are non-linear and even non-intuitive, with species-specific consumer and ecosystem responses that depend on the magnitude of temperature and nutrient changes as well as community composition.