Search ARMI Database
Search term(s)
Contribution Number
Search Results
180 record(s) found.
Papers & Reports Broad-scale assessment of methylmercury in adult amphibians
Papers & Reports Looking ahead, guided by the past: The role of U.S. national parks in amphibian research and conservation
Papers & Reports Research Needs to Inform Amphibian Conservation in the Anthropocene
Papers & Reports Complex life histories alter patterns of mercury exposure and accumulation in linked aquatic-terrestrial food webs: an amphibian example
News & Stories ARMI Scientists participate in first Global Amphibian and Reptile Disease Conference
The first Global Amphibian and Reptile Disease Conference was held in Knoxville, Tennessee in July 2022. ARMI scientists E. Muths and B. Hossack presented a synthesis of efforts to understand amphibian disease in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, and B. Hardy and L. Bailey, a PhD student and ARMI affiliate (respectively) at Colorado State University, presented a paper on the potential for demographic compensation in amphibian populations challenged by disease. These presentations were among the few field-based papers at the conference. ARMI scientists E. Grant and M. Bletz led one of the conference workshops to discuss and design conceptual disease models for major herpetofaunal pathogens. The aim of this workshop was to identify differences in knowledge, processes, and possible management strategies among host-pathogen systems. In addition, M.C. Hopkins, Wildlife Disease Coordinator, USGS Ecosystems Mission Area, was a member of the Scientific Committee for the conference.
The goal of the GARD conference was to engage a wide range of people, from scientists and students to veterinarians, natural resource managers, and policy makers, in sharing knowledge about various amphibian and reptile diseases and in working to identify disease management strategies that are applicable to herpetofauna conservation. This hybrid meeting hosted scientists from 25 countries, with presentations ranging from the research reports, including the roles of biodiversity and climate change in amphibian disease risk and amphibian disease immunogenetics, to broad keynotes, such as “Comparative ecology and evolution of reptile pathogens” and “Ranaviruses: four things we (mostly) know and three we (largely) do not”.
Papers & Reports Compensatory recruitment unlikely in high elevation amphibian populations challenged with disease
2. We use long-term mark-recapture data from five populations of boreal toads (Anaxyrus boreas boreas ), across an elevational gradient in Colorado, before and after pathogen arrival to assess whether populations can persist with Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd) via compensatory recruitment.
3. Prior to pathogen arrival, we found a life history tradeoff between survival and recruitment across elevations, where high elevation toads have high survival but lower recruitment and vice versa at lower elevations.
4. Pathogen arrival had a strong negative effect on apparent annual survival and recruitment leading to negative population growth rates and dramatically reduced host abundances. The data did not support the occurrence of compensatory recruitment.
5. Synthesis and applications. Our unique dataset indicates that demographic responses to pathogens may be environmentally (i.e., elevationally) context-dependent and highlights the value of long-term monitoring. We recommend that practitioners verify that potential persistence mechanisms occur across multiple populations and relevant environmental gradients to counter any assumptions of the mechanism existing species-wide. Quantifying variation in population responses to disease will aid in understanding the bounds of such persistence mechanisms and identify particularly vulnerable populations where mechanisms are non-existent.
Papers & Reports Captivity, reintroductions, and the rewilding of the amphibian microbiome
Papers & Reports Empirical evidence for effects of invasive American Bullfrogs on occurrence of native amphibians and emerging pathogens
threats to biodiversity. American Bullfrogs (Rana [Lithobates] catesbeiana),
which have been introduced to many parts of the world, are often linked with
declines in native amphibians via predation and the spread of emerging pathogens
such as amphibian chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis [Bd])
and ranaviruses. Although many studies have investigated the potential role of
bullfrogs in the decline of native amphibians, analyses that account for shared
habitat affinities and imperfect detection have found limited support for
clear effects. Similarly, the role of bullfrogs in shaping the patch-level distribution
of pathogens is unclear. We used eDNA methods to sample 233 sites in the southwestern USA and Sonora, Mexico (2016–2018) to estimate how
the presence of bullfrogs affects the occurrence of four native amphibians,
Bd, and ranaviruses. Based on two-species, dominant-subordinate occupancy
models fitted in a Bayesian context, federally threatened Chiricahua Leopard
Frogs (Rana chiricahuensis) and Western Tiger Salamanders (Ambystoma
mavortium) were eight times (32% vs. 4%) and two times (36% vs. 18%), respectively,
less likely to occur at sites where bullfrogs occurred. Evidence for the
negative effects of bullfrogs on Lowland Leopard Frogs (Rana yavapaiensis)
and Northern Leopard Frogs (Rana pipiens) was less clear, possibly because of
smaller numbers of sites where these native species still occurred and because
bullfrogs often occur at lower densities in streams, the primary habitat for
Lowland Leopard Frogs. At the community level, Bd was most likely to occur
where bullfrogs co-occurred with native amphibians, which could increase the
risk to native species. Ranaviruses were estimated to occur at 33% of bullfrogonly
sites, 10% of sites where bullfrogs and native amphibians co-occurred,
and only 3% of sites where only native amphibians occurred. Of the 85 sites
where we did not detect any of the five target amphibian species, we also did
not detect Bd or ranaviruses; this suggests other hosts do not drive the distribution
of these pathogens in our study area. Our results provide landscape-scale
evidence that bullfrogs reduce the occurrence of native amphibians and
increase the occurrence of pathogens, information that can clarify risks and
aid the prioritization of conservation actions.
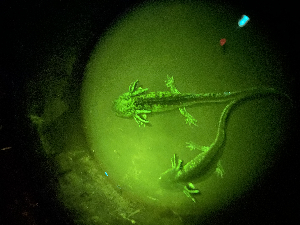
Papers & Reports Biofluorescence in tiger salamanders documented in Rocky Mountain National Park for the first time
News & Stories Dr. Cecil Schwalbe
Dr. Cecil Schwalbe passed away on 3 April 2022 from complications after a heart attack and pneumonia. Cecil was one of the early Principal Investigators for ARMI. His lab provided long term data from the desert southwest on summer breeding amphibians, bullfrog eradication, disease, and leopard frog conservation. Cecil’s work at Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge laid a foundation for additional ARMI efforts in expanding model development on occupancy, spatially explicit metapopulation theory, Chiricahua leopard frog survival, and habitat connectivity. ARMI post doc Richard Chandler and graduate students Chris Jarchow and Paige Howell led this work, but Cecil was supportive and interested in the research and how it contributed to conservation efforts (e.g., Chandler et al. 2015, Jarchow et al. 2016, Howell et al. 2016, 2018, 2019).
Cecil also contributed to collaborative ARMI efforts (e.g., Muths et al. 2005) and was always present at ARMI meetings to keep things field-oriented and to maintain an appropriate sense of humor. He retired from ARMI and the USGS in 2013, but remained active in the herpetological community. Cecil was an old-school herpetologist and while he would rather be investigating frog populations in the field or showing Gila monsters to school kids, he would thoughtfully listen to the reasoning behind monitoring protocols and models and provide input on field implementation for ARMI projects.
In addition to his PhD in zoology and physiology from the University of Arizona and a master’s degree from Washington State, Cecil held a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering from Rice University and was Arizona’s first State Herpetologist. His enthusiasm and dedication to conservation influenced many young scientists including some of us in ARMI. In recognition of his mentoring and influence, Cecil received the Jarchow Conservation Award in 1997 and the Charlie W. Painter Memorial Award in 2021 from SW Partners in Amphibian and Reptile Conservation.
Cecil is survived by his wife Carol, sons Adam and Ethan, two granddaughters, and his sister. The family requests that in lieu of flowers, donations be made in memory of Cecil, to the Cold-Blooded Research Fund in the School of Natural Resources and the Environment at the University of Arizona: https://give.uafoundation.org/cecilschwalbe. In keeping with Cecil’s profession and passion, the annual payout from this endowed fund will support research awards for undergraduate students, graduate students and faculty members who are studying amphibians, reptiles, or fish.
Cecil’s laugh and his off-color sense of humor will be missed by all of us and the herpetofauna that he cared about.